Overview¶
This section provides an overview of the Micro XRCE-DDS library. It is organized as follows:
DDS-XRCE protocol¶
eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS implements the DDS-XRCE protocol specified in the DDS for eXtremely Resource Constrained Environments standard as defined and maintained by the Object Management Group (OMG) consortium.
This protocol allows resource-constrained devices to communicate with a larger DDS (Data Distribution Service) network. This communication is based on a client-server architecture, where the server (XRCE Agent) acts as an intermediary between the clients (XRCE Clients) and the DDS Global Data Space.
The DDS-XRCE protocol defines the wire protocol between XRCE Agents and XRCE Clients. The messages exchanged revolve around operations and their responses. The XRCE Clients request the XRCE Agents to run operations, and the XRCE Agents reply with the result of the requested operations. Making use of these operations, the XRCE Clients can create the DDS entities’ hierarchy necessary to publish and/or receive data from DDS. The DDS entities are created and stored on the XRCE Agent’s side so the XRCE Clients can reuse them at will with subsequent operations requests.
eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS implements the DDS-XRCE protocol using an XRCE Agent as a broker and providing a C API for developing XRCE Clients applications. The Micro XRCE-DDS Agent uses eProsima Fast DDS to reach the DDS Global Data Space.
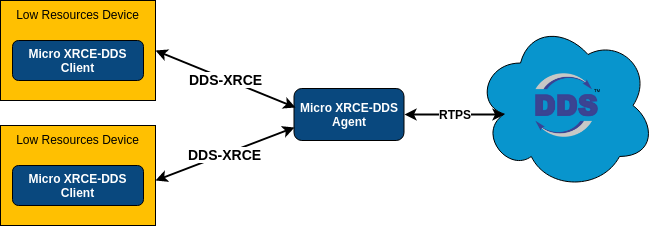
DDS standard and Fast DDS¶
eProsima Fast DDS is a C++ implementation of the DDS standard and makes underneath use of the RTPS (Real-Time Publish-Subscribe) wire protocol, which provides publisher-subscriber communications over unreliable transports such as UDP. Both the DDS specification and the RTPS protocol are defined and maintained by the OMG consortium.
For more extensive information, please refer to the official documentation: eProsima Fast DDS.
Operations and entities¶
The communication between XRCE Clients and XRCE Agents is based upon Operations and responses. Clients request operations to the Agents, which generate responses with the result of these operations. The Client, once informed back on the result of th requested operations, will be able to perform subsequent actions and/or request further operations.
The communication starts with a handshake for the Agent to acknowledge that a Client is present in the network. This happens via a Create session operation forwarded from the Client to the Agent, with which the latter registers the Client. Without registering a session, all the subsequent operations sent to the Agent will be refused. Once registered, the Client can request operations to the Agent, through which it can create and query entities. The communication with DDS is handled by the Agent using these Entities.
The Create entity operation is the request used to create entities in the Agent. Each of these entities corresponds to an eProsima Fast DDS object.
For sending and receiving data from/to DDS, the Client has access to the DataWriter and DataReader entities. These entities handle the writing/reading operations. For sending and receiving any topic, the Write Data and Read Data operations must be used.
To remove any entity from the Agent, use the Delete entity operation. Also, to log out a Client session from the Agent, use the Delete session operation.
Operations¶
Operations are the possible actions the eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS Client can request to the eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS Agent. Operations revolve around Entities. The eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS Agent will respond to all the requests with the status of the operation.
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
Create session |
With this operation Clients asks the Agents to register a session.
It is the first operation that must be performed. |
Delete session |
This operation deletes the Client-Agent connection and removes all entities associated with it.
After this operation, |
Create entity |
A session can create all the entities it needs. There is a Create entity operation for each entity the
session can handle. |
Delete entity |
Analogously, a session can delete the entities that were previously created on the Agent. To drop an entity, the entity ID must be used. |
Request Data |
This operation configures the data reception, which the Agent will deliver from the DDS data space to the Client.
Data are received |
Entities¶
The protocol underlying eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS (DDS-XRCE), defines entities that have a direct correspondence with their analogous actors on eProsima Fast DDS. The entities manage the communication between eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS Clients and the DDS Global Data Space. Entities are stored in the eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS Agent and the eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS Client can create, use and destroy these entities.
The entities are uniquely identified by an ID called Object ID. The Object ID is the way a Client refers to them inside an Agent. In most of the Client request operations it is necessary to specify an ID referring to one of the Client entities stored in the Agent.
Find below a table describing the entities the Client can interact with.
Entity |
Description |
|---|---|
Participant |
Participants can hold any number of Publishers and/or Subscribers. |
Publisher |
Publishers can hold any number of data writers. |
Subscriber |
Subscribers can hold any number of data readers. |
Topic |
Topic data is the base of the communication. A Topic is composed of a name and a data type. |
DataWriter |
This is the endpoint able to write Topic data. |
DataReader |
This is the endpoint able to read Topic data. |
Requester |
This is the endpoint able to write Request data and to read Reply data. |
Replier |
This is the endpoint able to read Request data and to write Reply data. |
This figure shows the entities hierarchy
The creation the entities listed above needs to be done using the DDS XML configuration of the object to create. The XML configuration follows the same rules as in eProsima Fast DDS.
The data sent by the Client to the DDS Global Data Space closely resembles that of eProsima Fast DDS. The Interface Definition Language (IDL) is used to define the type and must be known by the Client. Having the type defined as IDL, we provide the eProsima Micro XRCE-DDS Gen tool. This tool can generate a compatible type that the XRCE Client can use to send and receive. The type has to match the one used on the DDS Side.